Linksys 3102 for Dummies
Introduction
The Linksys SPA-3102 is the younger brother of Sipura's 3000. Sipura is now part of Linksys, which is itself part of Cisco. The main difference between the 3000 and the 3102 is that the latter can act as a NAT router. This is typically meant so you can connect your PC to the Linksys, and the Linksys to the LAN, without needing two LAN ports.
The 3102 unit offers the following features:
- ATA (to turn an analog handset into a poor man's IP phone and connect to a VoIP provider)
- VoIP gateway (to connect an SIP server to an analog phone line)
- Router + DHCP server
It's important to keep in mind of couple of things: This unit is...
- marketed towards VoIP providers, not end-users, hence the dearth of documentation public-available. Don't expect much help from Sipura's tech support, and none from Linksys. For help, forums and Google are your friends
- primarily meant to be used as an ATA, so the PSTN gateway is not on par with professional-grade gateways like Sangoma, etc. Some users occasionally complain of echo when connecting with the PSTN network. YMMV.
Making sense of the 3102
The 3102 has Internet and Ethernet ports because it can be used as a router between two networks, or more realistically, between the Linksys and your PC. Setting the Router > Lan to "Bridge" just turns it into a bridge, ie. both plugs use the same IP so you can then access the 3102 through either plugs.
Once the embedded web server is up and reachable, configuring the 3102 means making changes in the Voice tab while in Admin mode (Basic or Advanced):
- System: When you need to send logs to a syslog/debug server
- SIP: You might need to make changes to the RTP Parameters; The NAT Support Parameters are useful only when the 3102 is running as a router (which it isn't here, so don't change those settings). Ditto for the STUN settings, as the IP PBX server will take care of turning the 3102 private address/port into an Internet-reachable public setting
- Regional: This is where you must put locale telecom information, eg. dial tone, etc. It's especially important to set the disconnect tone right, so that the 3102 doesn't remain off-hook after you (think you) hung up...
- Line 1: If you use the 3102 as an ATA by plugging an analog handset to the Phone interface, you must enable this feature. Configure the ATA to register with the IP PBX server, and let the PBX handle the dialplan instead of the 3102
- PSTN Line: This is where you configure the PSTN interface so that the 3102 succesfully behaves as a PSTN gateway. Just like the ATA interface, make sure this interface registers with the IP PBX server, and let the PBX handle the dialplan, eg. (<:1001>S0) sends all incoming calls to extension 1001 on the IP PBX server
- User 1: Settings for the ATA interface
- PSTN User: Settings for the PSTN interface
Setup
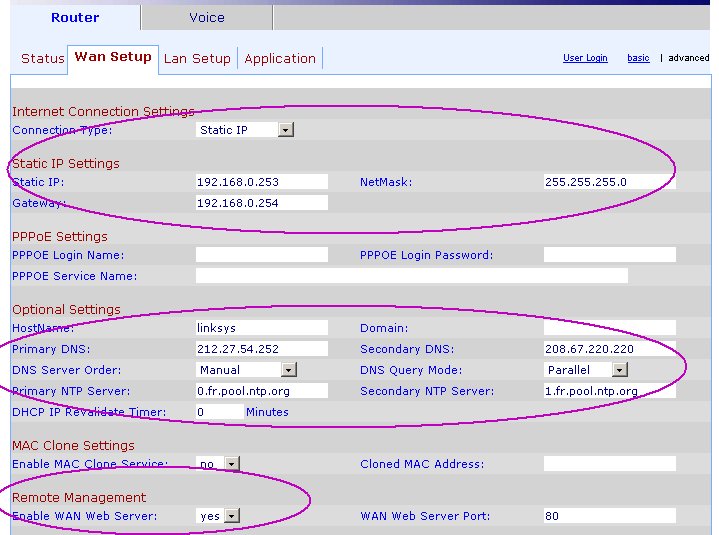
Important: If you already have a router, and hence, will use the 3102 as just a VoIP gateway, enable the WAN's web server, and use that port to plug the unit to the switch/hub. Alternatively, you can set the LAN from NAT to Bridge, and plug the unit using either the WAN or LAN interfaces ("Internet" or "Ethernet").
- Make sure the unit is connected to the switch through its blue Internet plug
- Connect a handset to the Phone plug, and type **** to enter the configuration menu
- To check the unit's IP address, dial 110#
- Dial 7932# followed by 1#, and 1 to enable access to the embedded web server through the Internet plug
- Aim your browser to http://linksys-ip/admin/voice/advanced . Some of the settings are country-specific, so you'll have to google or ask in forums for settings that those where you live.
- If you lost the admin's password, reset the unit with **** followed by 73738#, and confirm with 1
- The latest updates can be found here
- Sysros Syslog Desktop is a free syslog server for Windows
If you messed things up and can't connect to the embedded web server, unplug everything, power off the unit for at least 30 seconds to let capacitors drain, replug cables, and go through the above procedure to enable web access over the WAN port and get the IP address used by the unit.
One more thing: In some sections, the configuration of a 3102 differs depending on if you're going to use in stand-alone mode (the 3102 connects to a VSP directly) or with an IP PBX (the 3102 lets the PBX connect to the VSP), and whether there's NAT involved.
Router
WAN Setup
LAN Setup
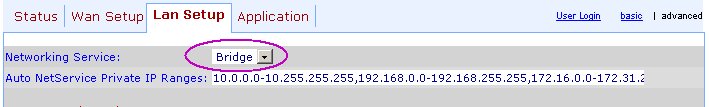
Once set as Bridge, you can connect the 3102 to the hub through its Internet or Ethernet port.
Voice
System
SIP
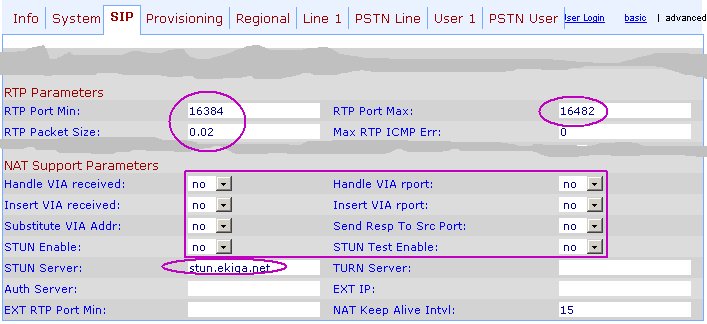
The RTP Port setting only matters if 1) the 3102 is located in a private LAN, 2) it either connects to a VSP directly or it goes through an IP PBX that is located in the public LAN, and 3) the NAT router doesn't support STUN so that you need to map ports to let incoming packets reach the 3102.
The settings in the "NAT Support Parameters" are not needed if you have an IP PBX in the private LAN to handle NAT issues, as the IP PBX will take of rewriting IP/port information accordingly. More information about this section here.
Regional (for France)
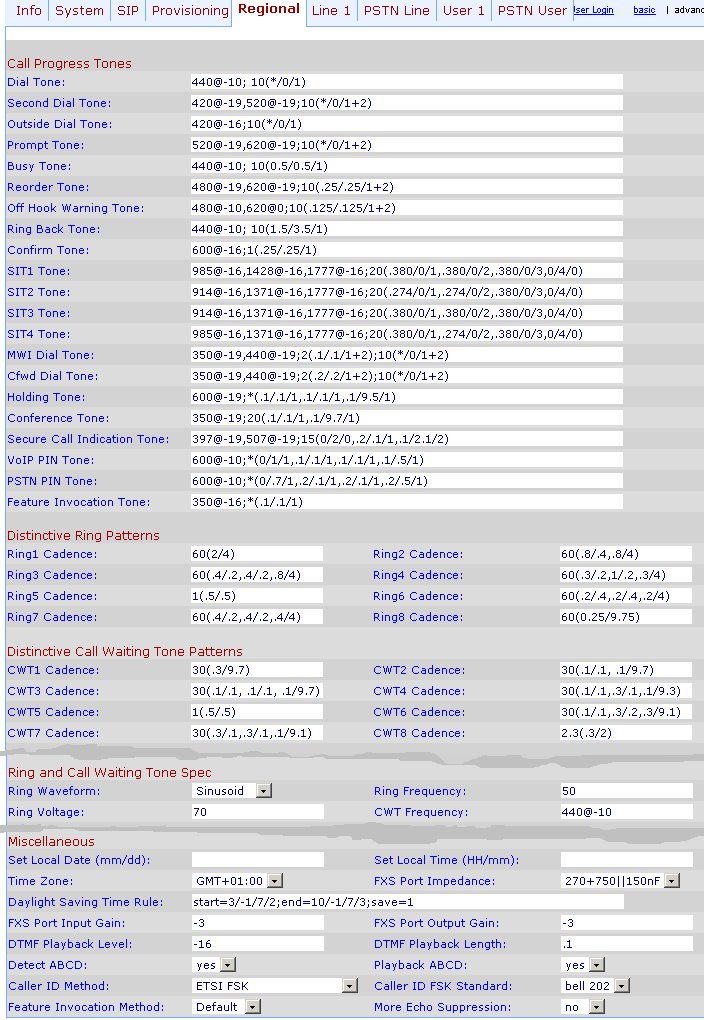
The FXS infos are only needed if you use the Phone plug to connect a handset. If the remote caller complains about echo, play with the "FXS Port Impedance", "FXS Port Input/Output Gain" settings.
More information about regional settings:
- http://www.3amsystems.com/wireline/tone-search.htm
- http://www.3amsystems.com/wireline/daa-search.htm
Line 1
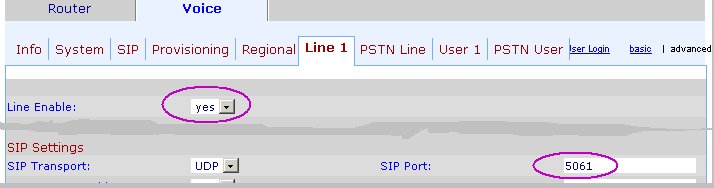
The Phone port (ie. FXS) and the Line port (ie. FXO) must have their own UDP port. Here, we'll use 5061 for the Phone port, and 5060 for the Line port.
PSTN Line
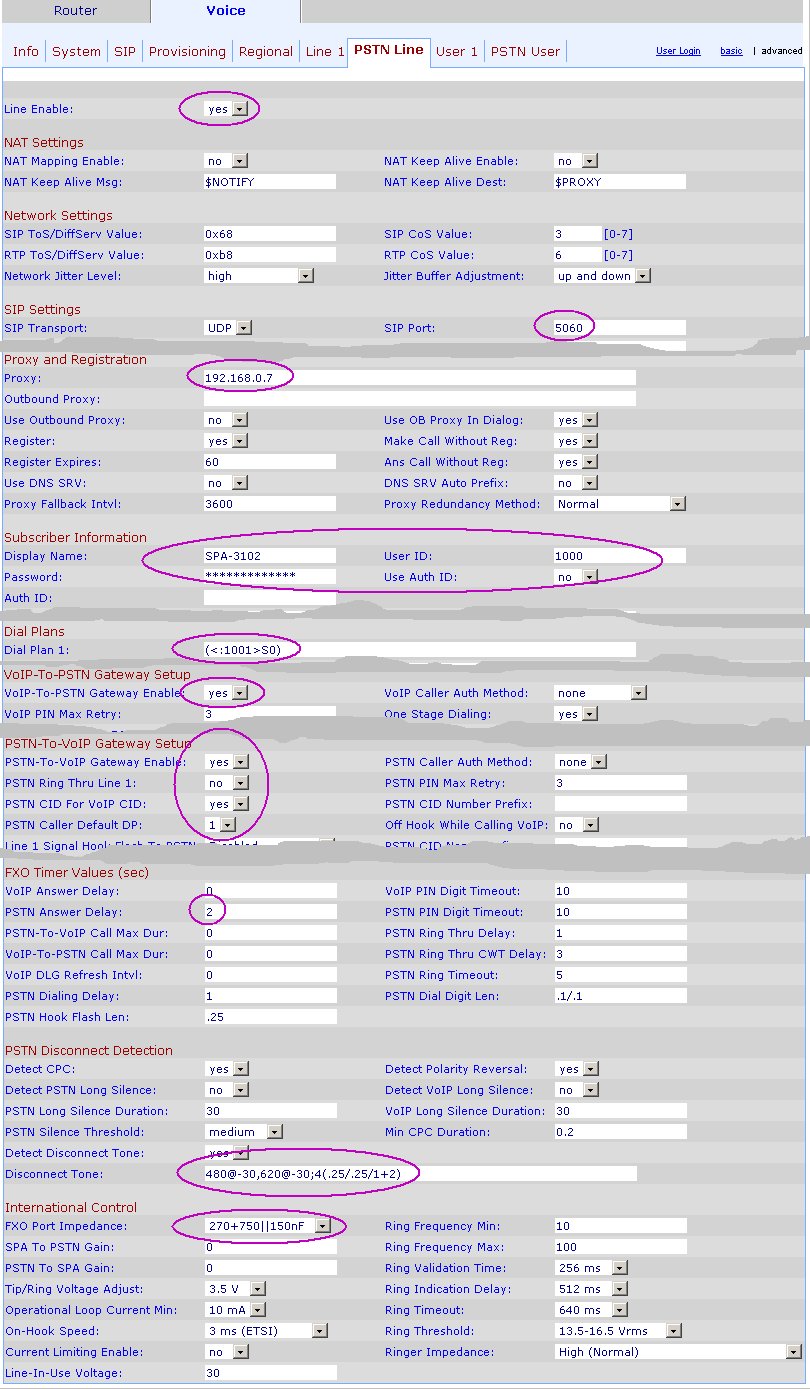
"PSTN Answer delay" is the number of seconds before the 3102 will call the IP PBX. This is needed to leave enough time for the 3102 to catch CID information.
The "<:1001>S0" dialplan means that incoming PSTN calls will call the 1001 extension on the IP PBX.
Make sure you use the right "Disconnect Tone" and "FXO Port Impedance" for your country.
In case of echo, play with the "SPA to PSTN Gain" and "PSTN to SPA Gain" settings.
Line-In-Use Voltage: Make sure it's lower than what it says in Voice > Info > Line Voltage: Otherwise, the Linksys will think that the line is already in use.
Adding a Linksys VoIP gateway to Asterisk
Here, we'll use an external box like the Linksys 3102 to act as VoIP gateway, ie. interface between a PSTN line and the network. If you only use SIP, you don't need to compile and configure zaptel and libpri. You'll just need to build sip.conf, extensions.conf, and voicemail.conf.
First, edit sip.conf to add an extension so the Linksys can connect to the Asterisk server:
- [fxo]
- type=friend
- secret=fxo
- qualify=yes ; Qualify peer is no more than 2000 ms away
- nat=no ; located in the same LAN as Asterisk
- host=dynamic ; This device registers with us
- canreinvite=no ; Asterisk by default tries to redirect
- context=internal ; the internal context controls what we can do
Next, edit extensions.conf to create a group extension so that incoming PSTN calls ring multiple phones:
- [internal]
- exten => 200,1,Dial(SIP/200)
- exten => 201,1,Dial(SIP/201)
- exten => 202,1,Dial(SIP/202)
- ;phone number that start with 0 are sent to Linksys -> landline
- exten => _0.,1,Dial(SIP/fxo)
- exten => group,1,Dial(SIP/200&SIP/201&SIP/202)
Finally, connect to the Linsys embedded web server, and go to Voice > PSTN Line to add the IP address of the Asterisk server in "Proxy and Registration" > Proxy, and fill the "Subscriber Information" section with the login/password set in sip.conf for the device.
Also edit the default dial plan "Dial Plan 1" under "Dial Plans" so that the Linksys knows which extension to call when it detects an incoming call:
- (S0<:group@IP-address-of-Asterisk-server>)
Launch Asterisk in console mode, type "reload" to... reload the configuration files, reboot the Linksys, and type "sip show peers" to check that the Linksys device registered correctly.
Now, call into the Linksys from a PSTN phone: The extensions listed in extensions.conf should ring.
Stuff I learned while trying to use a 3102 as a PSTN gateway on a private network, with remote IP phones behind their own NAT router and connecting to Asterisk:
- On the NAT router protecting Asterisk, you must open UDP5060 and route incoming packets to the Asterisk server; But when using STUN, you must change the 3102's default PSTN Line port from 5060 to something else, or you'll get a conflict since the port is already in use on the router ("STUN trying 0, STUN trying 1, STUN trying 0, STUN trying 1, etc.)
- STUN requests will be sent whenever STUN Test Enable YES is specified. If you specify STUN Test Enable NO the STUN requests are only sent if you also specify NAT Mapping Enable for the line.
- If the 3102 and Asterisk are both in the same LAN, do not set "NAT Mapping Enable" to "yes", or the Info > External IP will show the 3102's private address instead of the public IP on the Net
- In Voice > Info, check External IP, RTP Packets Sent/Recv, and SIP Messages Sent/Recv
- On the host running Asterisk, run tcpdump and/or wireshark to sniff packets
- tail -f /var/log/asterisk/messages
Error messages with firmware 5.1.7 while booting:
- <159>system request reboot
- <143>
- <134>++++ sip skt[0]= INVALID
- <134>++++ sip skt[0]= INVALID
- <151>[5061]STUN trying 0
- <159>IDBG: st-0
- <134>YM:ERR:AuthServerNotConfig
- <134>YM:ERR:AuthServerNotConfig
- <151>[5061]STUN trying 1
- <151>[5061]STUN trying 0
- <151>[5061]STUN trying 1
- <151>[5061]STUN trying 2
- etc.
Recent update to the 3000. Once you know its IP address by hooking up a phone to its PHONE interface and typing **** followed by 110#, make sure you uploaded the latest firmware to the unit.
Regional settings
Regional settings for France
References: http://www.itu.int/ITU-T/inr/forms/files/tones-0203.pdf, World PSTN Tone Database, and here.Information: "le codec standard (en Europe et dans le reste du monde, sauf en Amérique du Nord et au Japon) est le G711 a-law, appelé aussi PCMA; il correspond à un échantillonnage de la voix sur une échelle logarithmique, à une fréquence de 8 kHz et sur 8 bits (le codec standard utilisé en Amérique du Nord et au Japon étant le G711 µ-law, appelé aussi PCMU; la différence entre le PCMA et le PCMU réside, entre autres, dans la fonction d'interpolation) le débit correspondant à la voix est alors de 64 kbit/s - équivalent à une communication analogique -, tout le reste correspond à des overheads pour le transport sur la couche IP"
PSTN Line
- Detect CPC: YES
- Detect Polarity Reversal: YES
- Disconnect Tone: 440@-20,440@-20;1(0.5/0.5/1) (was: 480@-30,620@-30;4(.25/.25/1+2))
- FXO Port Impedance: 370+620||310nF (Valeur exacte: 180+910||150nF (non disponible) recommandation Sipura: 370+620||310nF (270+750||150nF?)) (was: 600)
- SPA To PSTN Gain: 0
- PSTN To SPA Gain: 0
- On-Hook Speed: 3 ms (ETSI) (was: Less than 0.5ms)
Regional
- Dial Tone: 440@-12;10(*/0/1) (was: 350@-19,440@-19;10(*/0/1+2))
- Second Dial Tone: 440@-12;10(*/0/1) (was: 420@-19,520@-19;10(*/0/1+2))
- Prompt Tone: 440@-12;10(*/0/1) (was: 520@-19,620@-19;10(*/0/1+2))
- Busy Tone: 440@-20;10(.5/.5/1) (was: 480@-19,620@-19;10(.5/.5/1+2))
- Reorder Tone: 440@-20;10(.5/.5/1) (was: 480@-19,620@-19;10(.25/.25/1+2))
- Off Hook Warning Tone: 440@-20;10(.5/.5/1) (was: 480@-10,620@0;10(.125/.125/1+2))
- Ring Back Tone: 400@-20;*(1.65/3.35/1) (was: 440@-19,480@-19;*(2/4/1+2))
- Ring1 Cadence: 2.25(.25/1.6);60(2/4) (was: 60(2/4))
- Ring2 Cadence: 2.25(.25/1.6);60(.3/.2,1/.2,.3/4) (was:60(.3/.2,1/.2,.3/4))
- Ring3 Cadence: 2.25(.25/1.6);60(.8/.4,.8/4) (was:60(.8/.4,.8/4))
- Ring4 Cadence: 2.25(.25/1.6);60(.4/.2,.3/.2,.8/4) (was: 60(.4/.2,.3/.2,.8/4))
- Ring5 Cadence: 2.25(.25/1.6);60(.2/.2,.2/.2,.2/.2,1/4) (was: 60(.2/.2,.2/.2,.2/.2,1/4))
- Ring6 Cadence: 2.25(.25/1.6);60(.2/.4,.2/.4,.2/4) (was: 60(.2/.4,.2/.4,.2/4))
- Ring7 Cadence: 2.25(.25/1.6);60(.4/.2,.4/.2,.4/4) (was: 60(.4/.2,.4/.2,.4/4))
- Ring8 Cadence: 2.25(.25/1.6);60(0.25/9.75) (was: 60(0.25/9.75))
- Ring Frequency: 50 (was: 25)
- Time Zone: GMT+1:00 (was: GMT -8)
- Daylight Saving Rule: start=3/-1/7/2:0:0;end=10/-1/7/2:0:0;save=1:0:0 (was: US)
- stun.fwdnet.net:3478
- Primary NTP Server: europe.pool.ntp.org
- Secondary NTP Server: pool.ntp.org
- Caller ID Method: ETSI FSK (was: Bellcore)
Playing with dialplans
Securing the 3102
Make sure no one can make calls from the Net to the PSTN line, or from the PSTN line to a VoIP gateway
No connection to the embedded web server from the Net
Reliable IP Phones
Those phones are known to work well, although they'll have the same issues if there's a non-VoIP-friendly NAT firewall in the way to the Internet...
- Siemens C470 IP
- Siemens A580 IP
- Thomson ST2030
- Linksys SPA942
- Linksys SPA962
Tips & Tricks
Checking the hardware
When turned off, the SPA3102 connects the Line to the Phone socket directly, so you can check that the hardware works by just plugging a handset in the Phone plug while the 3102 is off.
In case of echo when connecting to the PSTN line
If you're hearing your own voice, the problem lies at the other end of the line, in the analog section before voice is digitized at the Central office: "In a normal phone conversation, the latency is so low that you don't notice it. Your brain automatically tunes out to its own voice when you’re talking (as long as the delay between talking and hearing isn't too long)." Another cause for echo is how far you are from the Central office, which affects impedance and audio levels
Thus, if you hear echo of your own voice, the problem lies at the other end, and, short of getting the telco to improve their local loop, or the remote user to get a better phone and/or replace their shoddy cabling, there are three things you can try:
- Enable echo cancelling on your end so that your voice is removed from the RX signal just before it reaches you. If your IP PBX is connected to a POTS line, check the EC in your VoIP gateway; If it's a PCI card using the Zaptel/DAHDI interface, try different ECs, including OSLEC
- Check the TX gain on your phone (the TX signal even from IP phones can be too high for the Line Echo Canceller (LEC) in the POTS gateway). If you can, try another IP phone
- To reduce delay, try a low-latency codec like G711u, and short packet sizes.
If they hear their own voice, the problem lies at your end, and you can do the following things:
- Ideally, do not connect your IP PBX to a POTS line: Either use an ISDN
or E1/T1 line, or use a VoIP provider, which provides a digital gateway
to the telephone network.
If you do must connect it to a POTS line, use high-quality VoIP gateways by Digium, Sangoma, or Rhino, instead of cheaper solutions like the Minitar MVA11A or... the Linksys 3102. Also make sure its impedance settings match the line (impedance is country-specific). Other settings to try: input/output gain, jitter, RTP packet size - Do not use analog phones connected to ATA's, and use IP phones instead, either hardware or software
More information:
- Understanding VoIP Echo
- Echo in VoIP systems by Heison Chak
- Echo and Soft VoIP PBX Systems by David Mandelstam
- Echo Analysis for Voice over IP
- The SPA3102 and PSTN Call Quality Thread
Cheap line simulator
Take an RJ11 cable, plug one end into the FXS (Line1) port on your SPA, and the other end into the FXO (PSTN) port on the SPA. That way, you have a cheap PSTN line simulator which allows you to configure the caller ID standard (by changing the Line 1 settings). Calling the number people call to reach you on Line1, will then trigger a "PSTN" call that comes in to your PSTN port.
Q&A
Tunnel to IP PBX instead of STUN? OpenVPN with UDP?
Billion 7401VGPM
Router + VoIP
http://www.cormain.com.au/demo/B7401VGPM/default.htm
Linksys 3102 vs. Obi110?
http://nerdvittles.com/?p=720Linksys 3102 vs. Minitar MVA11A?
Caller ID is not showing
In the PSTN Line section, under FXO Timer Values, make sure PSTN Answer Delay is set to a value superior to 3 seconds.
If no caller ID name is sent by the telco, you can set what caller ID name will be sent to the PBX in the PSTN Line > Subscriber Information section (Display Name).
My syslogd is not getting debug information from Linksys
There are two locations under the Voice section:
- System > Miscellaneous Settings : Syslog Server and Debug Server:
- PSTN Line > SIP Settings : SIP Debug Option
- Line 1 > SIP Settings : SIP Debug Option
"When PSTN stops ringing, it takes a few seconds before my Line 1 stops ringing. Why?
The SPA rings a PSTN call through Line 1 by making an internal SIP call to Line 1. When PSTN ring stops, the SPA will take a few seconds to realize that the ring has truly stopped (due to some quiet period between rings), before it can tear down the corresponding internal SIP call to Line 1. This delay should be larger than the expected quiet period between 2 PSTN rings. You can configure this delay in the < PSTN Ring Timeout > parramter. The default value is 5 (s)."
Information
- While Linksys provides next to no information for the SPA-3102 (it's apparently marketed for VoIP providers, who have support contracts with Linksys), Sipura provides a lot more information for its older brother the SPA-3000
- Make sure the FXS and the FXO devices use different ports. Apparently, the SPA-3000 could use the same port, eg. 5060 for both, but the 3102 needs them to be different, eg. 5060 for the FXO and 5061 for the FXS
- Since software firmware 3.1.3, the default behaviour of PSTN to VOIP is to keep the PSTN line unanswered while it's forwarded to the VOIP extention.
- What I found is that the SPA would get unregistered after a while so when I call it will not be able to connect and obviously no CallerID will pass. What i did was reduce the registration time significantly lower (3600 to 120) as well as reduced the registration retry intervals (1200 to 1) so it will re-register much quicker. I assume that the quality of my connection has something to do with the regular unregistrations. Anyway its looking much better now
- To forward calls to a remote extension or SIP URL at the VoIP provider as set up in the Subscriber section, use Dial Plan 1: (S0<:voip_number>)
- You can set <PSTN-To-VoIP Gateway Enable> to "no". When disabled, incoming PSTN calls will not be auto-answered by the SPA. The PSTN call will still ring through Line 1 if <PSTN Ring Thru Line 1> is enabled.
- @gw0 is the reference to your FXO port. @gw1/@gw2/.. is a reference to your gateway X in the line1 configuration. They allow you to route a call to a different sip account and in case of @gw0 to the fxo port (pstn line)
- By default the SPA 3000 has the RTP packet size set to 0.030. This causes some poor sound qualities at times coming from Asterisk sound files. Change this to 0.020 and sound quality is excellent
- After an extensive reading on echo cancelization in Asterisk I figured out that if you reduced the SPA to PSTN gain the echo will go away. I set it to -4 and the echo is gone. Apparently the volume of the outgoing sound was creating more echo than the echo canceller could handle in the SPA
- "There is also another trap to avoid, when setting up G711a as the preferred codec you must be sure that "Use Pref Codec Only" is set to "no" otherwise the VOIP->PSTN and PSTN->VOIP will stop working. They namely use G711u and will not react on calls in G711a. Yet another undocumented feature!
- Next bump is the "PSTN Ring Timeout". It must be at least 1 second longer than the silent part of your PSTN ring cadence. In Sweden the ring cadence is 1s ring and 5s silence so here the ring timeout must be 6s. The symptons of a wrong value is that the Caller id turn to Anonymous after 1st ring and with a large gap the calls gets disconnected before you have time to answer them
- Next tip: If you haven't subscribed for CIP, set "CID Setting" to "no" to have a correct CID handling on a CIP-enabled telephone
- Unless the SIP devices support Symetric RTP, RTP requires two ports, one in each direction.
- "Your PSTN Line Voltage when the line is idle is only -21V, which is
much less than the industry standard -48V and is also beneath the 30V
point that the SPA uses to decide whether the PSTN Line is available
for use. In order to use your PSTN Line you will have to teach the SPA
that the PSTN Line's idle voltage is -21V.
To do this, go to the bottom of the PSTN Line page and change the value of "Line-In-Use Voltage" from 30 to 15. Now, when the voltage is more than 15 (as -21V is) the SPA will know it is safe to grab the line and use it and if the voltage is less than 15 (your line in use voltage should be about -9V) it will know that another extension phone is using the line and will not try to grab it." - "As I've said quite often here, -48V is industry standard for telephone battery. If you are seeing a positive reading it indicates that the jack you are plugged into is wired backward. This won't directly cause any pain with the SPA-3000/3102, but will manifest itself in diminished performance and/or feature failure if you use a 2-line (or "more"-line) phone and try to connect lines with different polarities on the ports."
- "The SPA-3000 is two independent ATAs in one box. For "Line 1 to @gw0" and "PSTN Line Ring Thru to Line 1" functionality, the SPA-3000 actually places a VoIP call from one side of the box to the other. Since bandwidth conservation is not a factor inside the SPA device, the SPA uses the G.711 CODEC for this call. If you have chosen any other CODEC as your preferred CODEC and have restricted the SPA to only use that CODEC you have effectively disabled the crossover functionality you desire."
How to make direct IP calls with a Linksys 3102?
GrandStream : "Note:- You will need to have SIP
Server field blank, along with NAT traversal set
to NO, no STUN Server configured and
... so as to avoid using an SIP PBX, and just have the Linksys ring a remote IP phone through the Net when a PSTN call comes in?
Enable IP Dialing Enable IP Dialing no
Note: If IP dialing is enabled, one can dial [user-id@]a.b.c.d[:port], where "@", ".", and ":" are dialed by entering "*", user-id must be numeric (like a phone number) and a, b, c, d must be between 0 and 255, and port must be larger than 255. If port is not given, 5060 is used. Port and User-Id are optional. If the user-id portion matches a pattern in the dial plan, then it is interpreted as a regular phone number according to the dial plan. The INVITE message, however, is still sent to the outbound proxy if it is enabled.
- http://www.sipura.com/support/spa3000faq/Section_2.html#2
- http://www.sipura.com/support/spa3000faq/Section_2.html#3
- http://www.sipura.com/Documents/faq/Section_2.html#3
- http://www.sipura.com/support/spa3000faq/Section_4.html#4
- http://faq.sipbroker.com/tiki-index.php?page=Inbound%20Calls%20Directly%20to%20your%20LinkSys%20or%20Sipura
- http://voip.wikispaces.com/IPDialling
- http://www.freeworlddialup.com/
- http://sipphone.com
Provisioning tab: Should I disable this?
You only need to disable this if you're having problems with settings (particularly dial plan) reverting to vendor defaults every 24 hours. If the Profile Rule is the default (shown below), leave it.
Profile Rule: /spa$PSN.cfg
I would disable it. It is mostly used by voip providers to remotely configure the adapter.Recommended settings for France
Set Time Zone to "GMT+01:00"
DST : start=3/-1/7/2;end=10/-1/7/3;save=1
The ATA Administration Guide has a lengthly discussion of the setting. I fussed with it and eventually got it to work after I put save=+1.You can setup an NTP server on one of the Router tabs so the adapter will get the correct time from an Network Time Protocol server when you boot it up.
"FXO Timer Values (sec)", "PSTN Disconnect Detection", "International Control": What are recommended settings for France?
Linksys ATA Administrator Guide
Parameters that pertain to the pstn line attached to the FXO port of the adapter.The ATA Administration Guide
is the basic technical manual for the SPA3102. The manual has impedance
and disconnect tone settings for France. Other regional tone settings
will work with the default settings, however changes can be made to
them so the sound is similiar to local settings. The Voxilla site used
to have a "localization wizard" but it looks like that is now gone. The
"3am" database has tone settings for a number of countries.
PSTN settings for France here.
Also, French progress tones (Dial, Busy, etc.) here.
This Voxilla site has a useful configuration wizard for a SPA3102 with Asterisk.
XLite issues
In incoming PSTN calls, how to rewrite CID so that XLite displays the actual caller's ID instead of the 3102 extension?
In outgoing PSTN calls, XLite says "Connected" although the 3102 is still dialing/ringing a remote PSTN number
How does SIP work
http://www.sipcenter.com/sip.nsf/html/What+Is+SIP+Introduction?'s for Voice items
Line1/PSTN Line
- Line 1/PSTN Line: Make Call Without Reg, Ans Call Without Reg
- Line 1: Dial Plan = (xx.)?
- Are NAT- and dialplan-related settings (SIP, Line1, PSTNLine) useless when using an Asterisk server?
- Are "PSTN-to-VoIP" and "VoIP-to-PSTN" useful even when using an Asterisk server, and allowing registered SIP users to make calls to the POTS, or having the POTS ring SIP extensions?
PSTN Line
To allow incoming PSTN calls to ring an IP PBX server, you must enable "PSTN-to-VoIP Gateway", and configure the "Proxy and Registration", "Subscriber Information". Apparently, there's no need to add anything else (eg. PIN number + dial plan)
What are the "User1" and "PSTN User" tabs?
User1 are settings for the Line1 port. PSTN User are settings for the PSTN Line port.
User1
- User 1 = handset connected to Line1/FXS port?
PSTN User
- PSTN User = any user (FXS or VoIP) trying to acccess FXO port?
- RTP Port Min/Max (Must be port-mapped on NAT router, or can 3102 punch holes itself?)
- NAT Support Parameters : what is VIA?
- STUN Test Enable = ?
- EXT IP?
- EXT RTP Port Min
- FXS Port Impedance = 600
- Register = ?
- Make/Ans Call Without Reg = ?
- Dial Plan = ?
- VoIP-To-PSTN Gateway Enable = ?
- PSTN-To-VoIP Gateway Enable = ?
- Can Line1 not use its own dial plan and always use the FS server's dial plan?
What is the "NAT Support Parameters" section, including the VIA information?
These settings offer various methods for the SPA3102 to discover its own external IP address which is necessary for some type of VoIP calls, specifically IP Dialling.
The only settings you might need to use here are STUN Enable and STUN Server but if your VoIP is already working properly leave them alone.
If you have a static IP address you can use EXT IP in this section to enter the IP address.
Different settings for the adapter to help the adapter to determine its external ip address and external port number. Good description here.What are "SIP Port" and "EXT SIP Port" for?
SIP Port is the current SIP port and EXT SIP Port allows you to specify (force) the external SIP port.
These are parameters on the Line 1 and PSTN tab used to set the sip port address for the adapter. I haven't seen EXT SIP port used.PSTN Line Section: NAT Settings
NAT Mapping Enable is whether to use the adapter's internal network address or external ip address (if the adapter can figure it out) in the sip messages. If your Asterisk server is on the same local network as the SPA3102 you would not use this setting.NAT Keep Alive Enable is whether or not to send a message every 15 seconds to the proxy to keep your sip port open in your local router for an incoming call.
PSTN Line section: Proxy and Registration: What are "Outbound proxy" (to use a different server for outbound calls?), "Use OB Proxy in Dialog", and "Make/Ans Call Without Registration"?
Only change these if advised by your VSP.
To give you the flexibility to use a different proxy or domain from the registration proxy.What are "VoIP-To-PSTN Gateway Setup" and "PSTN-To-VoIP Gateway Setup"?
Control incoming (PSTN-To-VoIP) and outgoing (VoIP-To-PSTN) PSTN calls and other advanced stuff. Just make sure that both Gateways are enabled.
Parameter settings for the bridging of calls between incoming/outgoing calls on the FXO port and voip.Resources
- Sipura Support
- Linksys Support
- Whirlpool
- Cisco Community Central - SPA ATA and Gateway Documentation
- BroadBand > Forums > Voice Over IP - VOIP > VOIP Tech Chat (including [Equipment] Useful Sipura tricks)
- Voxilla > Linksys (Sipura) SPA Users Group
- news://comp.dcom.voice-over-ip
- WinSTUN is a Windows GUI utility to check that your NAT router supports STUN (Note: "Does not support hairpin of media" means that the NAT is unable to redirect RTP packets to the other SIP client when both are located on the same side of the NAT router).
More information:
- Linksys SPA3102
- Linksys ATA Administrator Guide 3.2.pdf (includes a description of all items in the different tabs; covers PAP2T, SPA1001, SPA2102, SPA3102, RTP300, WRTP54G)
- SPA-3000 Simplified Guide (discussion) and Sipura SPA-3102 Simplified Users Guide Version 1.1a
- Sipura Documentation SIP (including on NAT settings)
- SIP, Session Initiation Protocol
- SIP and NAT - An Introduction
- (French) Comprendre les échanges SIP par l’expérimentation
- (French) Configuration Voip sur LINKSYS SPA-3102
- To configure the 3102 as a PSTN-to-PBX SIP gateway when you already have a router, read Linksys SPA-3102 FXS/FXO
- Linksys SPA-3102 – Asterisk configuration HOWTO
- Voxilla FAQ > Sipura SPA Series, including What impedence setting should I choose for my SPA-3000 FXO port?
- Sipura 3000 System Tray Monitor
- SPA-3000 Configuration Setup Page
- Dial Plan Generator For Sipura 3000
- Useful Stuff for your SPA-3000 VoIP Gateway
- Voice quality on the Linksys
- http://forums.linksys.com/linksys/board?board.id=VoIP_Adapters (not much traffic)
- Linksys SPA3000/3102 Configuration Wizard for Asterisk at voxilla.com
- World PSTN Tone Database
- SPA-3000 PSTN-Line config for France
- French locale settings
- Configuration d'un ATA Sipura et Routeur/Firewall Netgear
- Step by Step Introduction by Jason from JMG Technology
- FXO Adapters Installation Guide
- Eliminating Echo Problems in SPA-3000
- "BroadTel RPA-2E1S1O is a better alternative and the best buy in the market."
- Setup a Linksys/Sipura SPA-3000 with FreePBX
- VoIPInfo > Sipura 3000
- VoIPInfo > NAT/Via stuff
- How do I craft a dial plan string?
- LinkSys and Sipura dial plans
- Setup Guide for using your SPA3000 / SPA3102 FXO adapter with Axon
- AXON & FXO (SPA3000), PRoblems! Can't get to work!
- "SIGVIEW is a real-time signal analysis software package with wide range of powerful FFT spectral analysis tools, statistics functions and a comprehensive visualization system."
- Linksys support: Forwarding PSTN Calls to a VOIP number on SPA-3102, What is a Dial Plan and how to configure it?, Getting to Know Dial Plan Parameters, Getting to Know Dial Plans Sequences
- Configuring Linksys 3102 for 3CX Phone System